Introduction to https://finanzasdomesticas.com/euribor-sube/
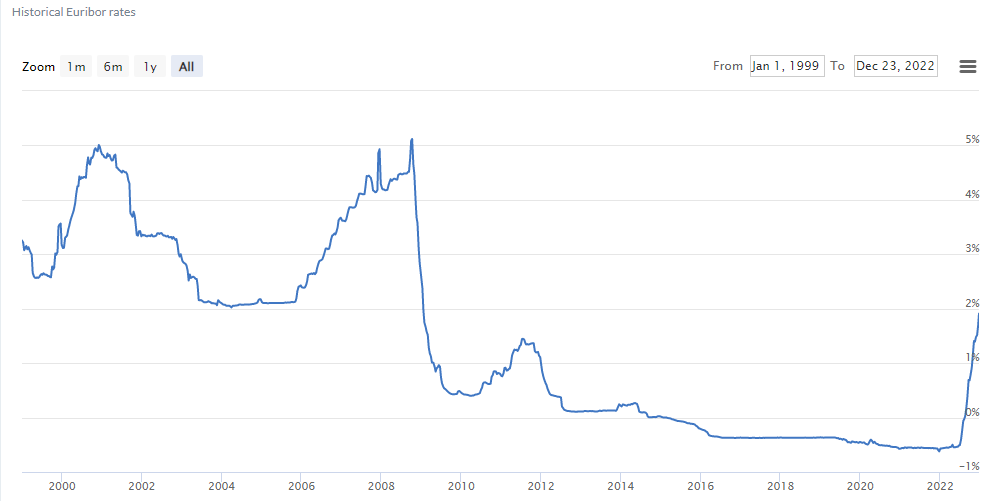
The Euribor (Euro Interbank Offered Rate) has been making headlines lately due to a significant increase in its value. This benchmark interest rate, which is used to determine the cost of borrowing between banks in the eurozone, has a direct impact on various financial products, including mortgages, loans, and savings accounts. In this blog post, we’ll explore what the Euribor increase(https://finanzasdomesticas.com/euribor-sube/) means for you and your finances.
Understanding the Euribor
The Euribor is a set of interest rates that reflect the average cost at which banks in the eurozone lend to one another. It is calculated daily for different maturities, ranging from one week to one year. The Euribor serves as a reference rate for numerous financial instruments and is closely monitored by financial professionals and individuals alike.
Causes of the Euribor Increase
The recent rise in the Euribor can be attributed to several factors:
- Monetary policy changes: The European Central Bank (ECB) has been gradually increasing interest rates to combat high inflation in the eurozone. As the ECB raises its benchmark rates, the Euribor follows suit.
- Economic recovery: As the eurozone economy recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic, demand for credit is increasing, putting upward pressure on interest rates.
- Geopolitical tensions: Global events, such as the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine, have contributed to economic uncertainty and volatility in financial markets, leading to higher borrowing costs.
Impact on Mortgages and Loans
One of the most significant impacts of the Euribor increase is on variable-rate mortgages and loans. If you have a mortgage or loan that is tied to the Euribor, your monthly payments will likely rise as the Euribor increases. This can put a strain on household budgets and make it more difficult to manage debt.If you are considering taking out a mortgage or loan, it’s important to factor in the potential for higher interest rates in the future. Fixed-rate mortgages may become more attractive as the Euribor rises, as they offer stability and predictability in your monthly payments.
Effect on Savings Accounts
While the Euribor increase (https://finanzasdomesticas.com/euribor-sube/) may be bad news for borrowers, it can be good news for savers. As banks face higher costs of borrowing from one another, they may pass on these higher rates to depositors in the form of higher interest rates on savings accounts. This means that your savings could potentially earn more interest as the Euribor rises.However, it’s important to note that the increase in savings rates may not be as significant or immediate as the increase in borrowing rates. Banks may be hesitant to raise deposit rates too quickly, as this can impact their profitability.
Implications for Businesses
The Euribor increase also has implications for businesses that rely on short-term financing or have variable-rate loans. As the cost of borrowing rises, businesses may face higher interest expenses, which can eat into their profits. This can lead to higher prices for consumers or even job cuts as businesses try to reduce costs.Businesses that are heavily reliant on credit may need to rethink their financing strategies and explore alternative sources of funding, such as equity financing or longer-term fixed-rate loans.
Monitoring the Euribor
Given the importance of the Euribor in the eurozone financial system, it’s crucial to stay informed about its movements. You can monitor the Euribor rates on various financial websites and news sources. It’s also a good idea to regularly review your financial situation and make adjustments as needed to adapt to changes in interest rates.
In conclusion, the increase in the Euribor is a significant development that has implications for borrowers, savers, and businesses in the eurozone. By understanding how the Euribor works and its impact on various financial products, you can make informed decisions to protect your finances and take advantage of opportunities presented by rising interest rates.
Influence small businesses and startups
High Euribor rates can significantly influence small businesses and startups in various ways, primarily through increased borrowing costs and restricted access to funding. Here are the key impacts:
1. Increased Borrowing Costs
As Euribor rates rise, the cost of borrowing also increases. This affects small businesses and startups in several ways:
- Higher Loan Repayments: Businesses with existing loans linked to Euribor will face higher interest payments, impacting cash flow and profitability. For startups, this means that initial financing costs become more burdensome, potentially delaying growth and expansion plans.
- Costlier Credit: New loans and credit lines will also come at a higher cost, making it more expensive for small businesses to finance operations, invest in new projects, or manage day-to-day expenses. This can lead to tighter budgets and reduced operational flexibility.
2. Restricted Access to Funding
High Euribor rates can lead to more stringent lending conditions:
- Lender Hesitance: Banks may become more cautious in their lending practices, particularly for startups that are perceived as higher risk. This can result in a reduced willingness to provide loans or credit to new ventures, making it harder for startups to secure necessary funding.
- Impact on Growth Plans: With limited access to affordable financing, small businesses may be forced to delay or scale back growth initiatives. This can hinder their ability to innovate or expand into new markets, ultimately affecting their long-term viability.
3. Economic Slowdown Effects
High Euribor rates (https://finanzasdomesticas.com/euribor-sube/) can contribute to a broader economic slowdown, which can further impact small businesses:
- Decreased Consumer Spending: As borrowing costs rise, consumers may reduce spending, leading to lower sales for small businesses. This can create a cycle of reduced revenue and tighter cash flow, further complicating financial management for startups.
- Increased Operational Costs: Rising interest rates can also lead to higher costs for materials and services, compounding the financial strain on small businesses already grappling with increased loan repayments.
4. Long-term Investment Hesitance
The uncertainty associated with high Euribor rates may lead to a cautious approach toward long-term investments:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Small businesses may prioritize short-term financial stability over long-term investment opportunities, which can stifle innovation and growth in the sector. This hesitation can affect their competitive edge in the market.
- Impact on Hiring: With tighter financial conditions, businesses may be less inclined to hire new employees or invest in employee training and development, which can limit their growth potential and adaptability in a changing market.
Long-term Effects of High Euribor Rates
1. Increased Borrowing Costs
High Euribor rates lead to higher interest rates on loans, including mortgages and business loans. This can result in:
- Reduced Consumer Spending: As borrowing costs rise, consumers may cut back on spending, particularly on big-ticket items that often require financing, such as homes and cars.
- Decreased Business Investment: Higher rates can deter businesses from taking loans for expansion or capital investments, potentially slowing economic growth and innovation.
2. Impact on Housing Market
The housing market is particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates:
- Lower Demand for Mortgages: As mortgage rates increase, fewer people may be able to afford new homes, leading to a slowdown in the housing market. This can result in lower home prices and reduced construction activity.
- Increased Financial Strain on Homeowners: Existing homeowners with variable-rate mortgages may face higher monthly payments, leading to financial strain and an increase in defaults or foreclosures if rates remain high for an extended period.
3. Economic Growth Slowdown
High Euribor rates can contribute to a general slowdown in economic growth:
- Tighter Financial Conditions: As borrowing becomes more expensive, overall financial conditions tighten, which can lead to reduced economic activity and slower GDP growth.
- Potential for Recession: If high rates persist, they could push the economy into recession, particularly if combined with other negative economic indicators such as high inflation or rising unemployment.
4. Effects on Inflation
While high Euribor rates are often a response to rising inflation, their long-term presence can have mixed effects:
- Potential for Lower Inflation: Higher interest rates can help control inflation by reducing consumer spending and business investment, which may stabilize prices in the long run.
- Stagflation Risk: However, if the economy slows significantly due to high rates while inflation remains elevated, it could lead to stagflation—an economic condition characterized by stagnant growth and high inflation.
5. Changes in Investment Behavior
Investors may alter their strategies in response to high Euribor rates:
- Shift to Safer Investments: Higher interest rates can make fixed-income investments more attractive, leading to a shift away from equities and riskier assets.
- Increased Market Volatility: As investors adjust to changing interest rates, financial markets may experience increased volatility, affecting overall market stability.
Conclusion
The Euribor increase (https://finanzasdomesticas.com/euribor-sube/) in the eurozone has significant implications for borrowers, savers, and businesses. Higher borrowing costs will increase monthly payments for variable-rate mortgages and loans, straining household budgets and complicating debt management. This rise also offers benefits for savers, as banks may raise interest rates on savings accounts. Small businesses and startups could face higher borrowing costs and limited funding, impacting their operations and daily expenses. In the long term, elevated Euribor rates may slow economic growth, reduce consumer spending, decrease business investment, and potentially lead to a recession. Staying informed about the Euribor is crucial for protecting finances and taking advantage of rising interest rates.
Also Read: https://notipostingt.com/2022/04/27/que-ver-y-hacer-en-isla-de-gozo
FAQs
What is the current Euribor rate?
The current Euribor rates can be found on the Euribor-rates.eu website. As of August 2024, the Euribor rates are:
- Euribor 1 week: 3.621%
- Euribor 1 month: 3.595%
- Euribor 3 months: 3.560%
- Euribor 6 months: 3.367%
- Euribor 12 months: 3.139%
How often does the Euribor change?
The Euribor is calculated and published daily by the European Money Markets Institute (EMMI). The rates can fluctuate based on various economic factors, such as monetary policy decisions, inflation, and market sentiment.
How does the Euribor differ from LIBOR?
The Euribor is the benchmark interest rate used in the eurozone, while LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) was the benchmark used in the United Kingdom and other countries. LIBOR was phased out in 2023 and replaced by alternative reference rates, such as SOFR in the US and SONIA in the UK.
Can I use the Euribor to predict future interest rates?
While the Euribor is a useful indicator of current borrowing costs in the eurozone, it’s not a perfect predictor of future interest rates. Many factors can influence interest rates, including economic growth, inflation, and central bank policies. It’s important to consider multiple sources of information when making financial decisions.
How can I protect myself from rising interest rates?
If you have a variable-rate mortgage or loan, you may want to consider refinancing to a fixed-rate product to lock in a lower interest rate. For savers, it’s a good idea to shop around for the best interest rates on savings accounts and to diversify your investments to mitigate the impact of rising rates.